Infrared Sensor Dispensers
Reduce touchpoints and support infection control plans by standardizing hand hygiene at fixtures. Consistent metered dosing lowers soap waste, simplifies O and M forecasting, and improves restroom throughput in peak occupancy periods while aligning with facility risk mitigation protocols for modern spaces.
Infrared sensor dispensers are widely used in commercial restroom programs where predictable maintenance and high-traffic performance matter. This page covers how they work, what to specify, and real-world performance criteria that impact hygiene outcomes and maintenance outcomes.
Why infrared sensor dispensers are being standardized in commercial restrooms

Reduced contact at high-touch hygiene points
The dispenser is one of the most frequently used hygiene touchpoints in restrooms. Replacing manual actuation with infrared activation reduces hand contact at that location, which supports facility infection control planning and surface cleaning strategies.
Metered dosing reduces waste and stabilizes usage forecasting
Infrared models can be designed for metered output. Instead of variable user-controlled pumping, the dispenser runs a timed dose. This improves soap usage predictability, refill forecasting, housekeeping planning, and waste reduction.
Restroom throughput improves during peak occupancy conditions
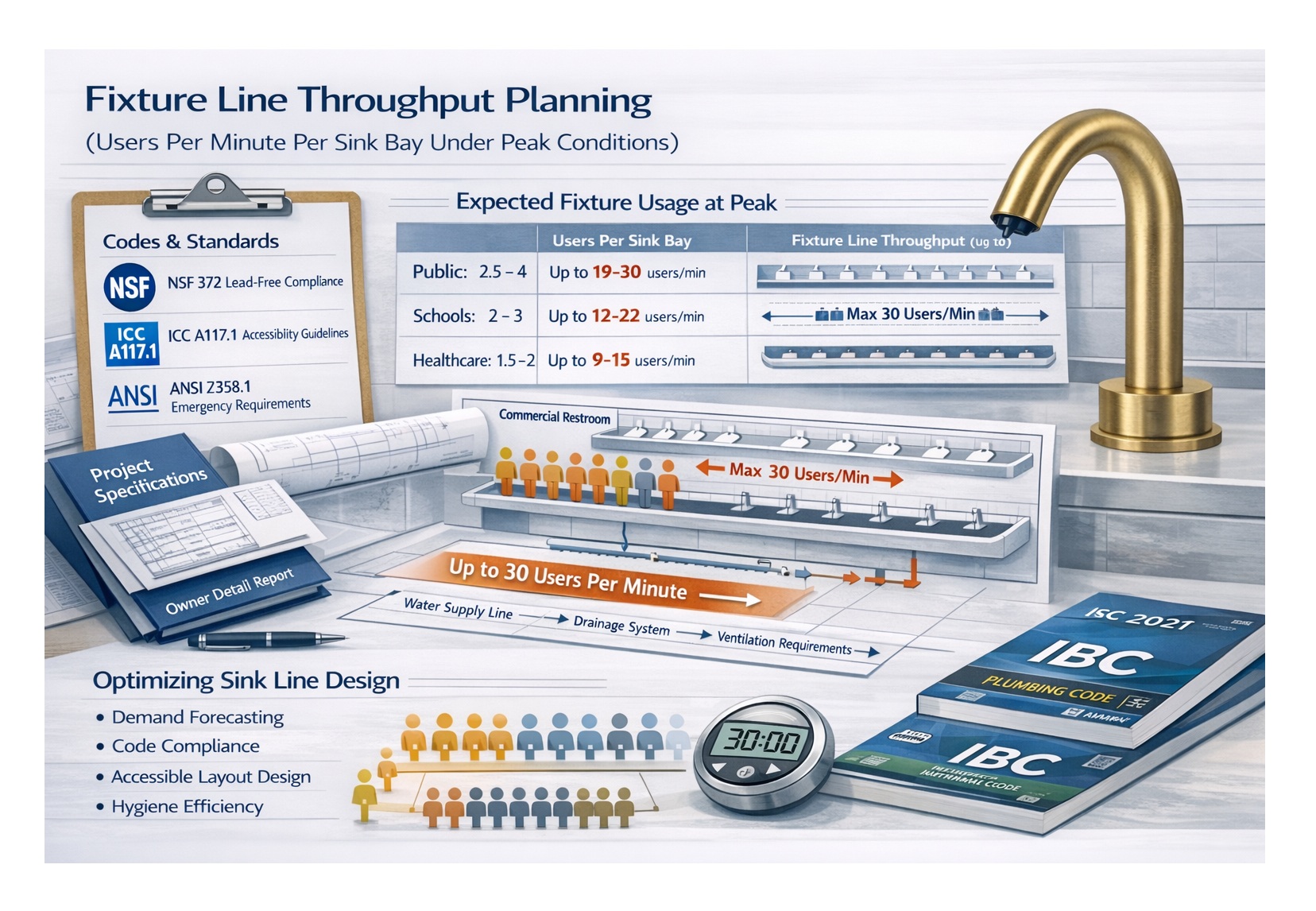
For high-traffic facilities like airports, schools, stadiums, and convention centers, throughput is a major design constraint. Touchless dispensing reduces friction in the wash sequence and keeps user movement more continuous, especially when paired with sensor faucets and touchless drying.
Operating Principle of Infrared Sensor Dispensers
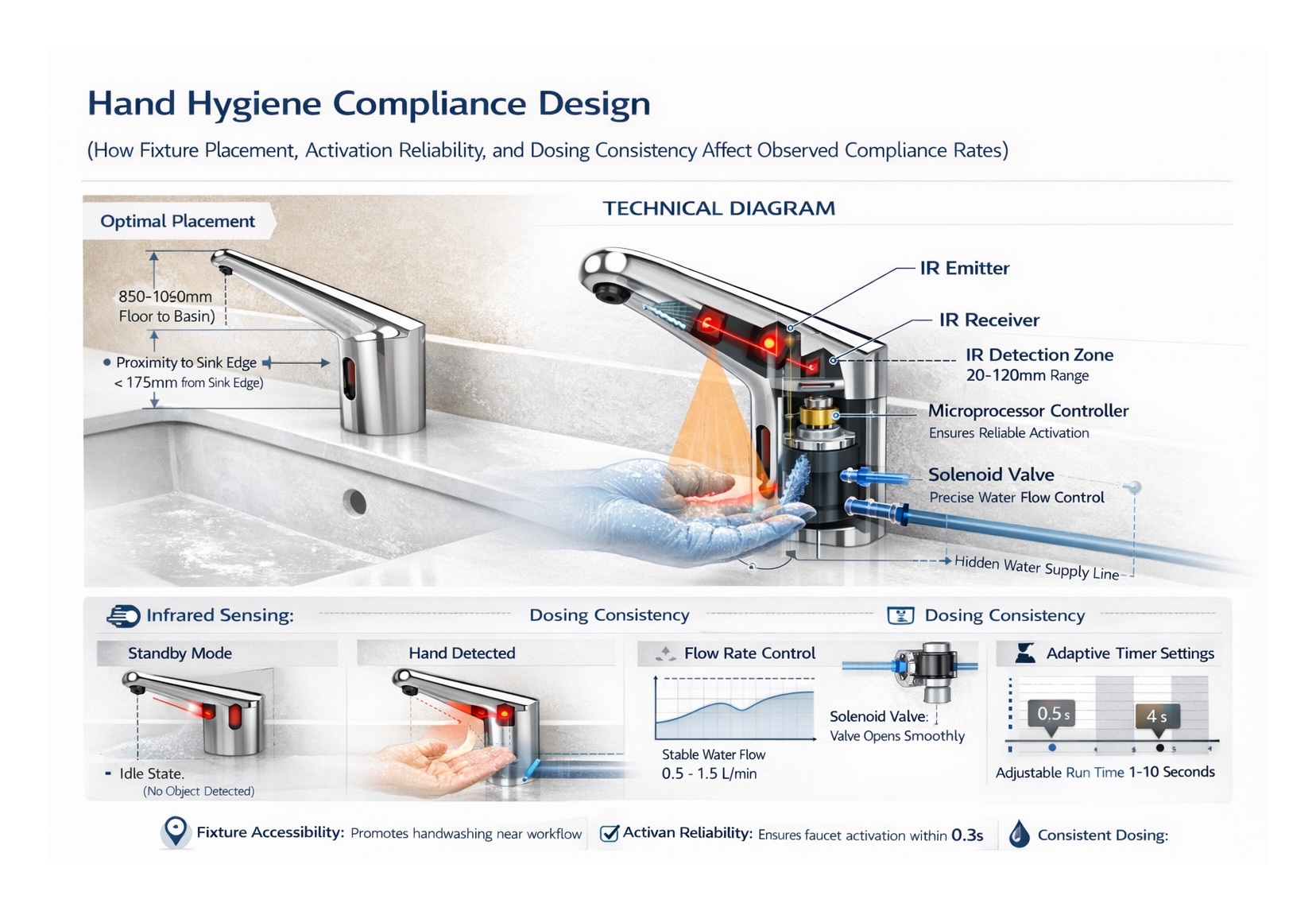
Most commercial infrared dispensers use active infrared proximity sensing by combining an IR emitter, an IR receiver, and firmware logic that interprets reflected IR energy. When a hand enters the detection zone, reflected IR is detected and the controller initiates a pump cycle for a predetermined dose.
Core system elements
- Sensor assembly: near-infrared emitter and receiver, protective lens, and detection filtering logic
- Controller: trigger threshold logic, cycle timing, lockout delay, and power management
- Pump system: diaphragm, peristaltic, or gear pumps depending on viscosity and drip control needs
- Fluid path: bulk reservoir dispensing or sealed cartridge refills
Field Performance Constraints in Real-World Deployments

False triggers and nuisance activation
False triggers cause soap waste, countertop mess, increased housekeeping labor, and user frustration. They often occur due to reflective surfaces, strong sunlight, high movement zones near the sensor, or splashing that interferes with the sensor window.
Missed triggers and slow activation
Missed triggers are commonly tied to short detection zones, poor sensor aim alignment, soap residue on the sensor window, or low battery power. Inconsistent activation can cause users to skip soap entirely.
Fluid compatibility problems
Not every soap is compatible with every pump system. Viscosity and refill format can affect dosing stability. In the field, inconsistent dosing is often tied to using an incompatible soap type or inconsistent refill product.
AEC Specification Criteria

Metered dosing consistency
- Consistent dispensing volume per activation
- Stable output across battery life range
- Minimal drip after actuation
Detection zone control
- Stable detection distance for one-handed activation
- Limited sensitivity to pass-by movement
- Anti-repeat lockout to prevent multiple dispenses per hand entry
Refill strategy aligned with facility policy
Bulk refill systems can reduce unit cost but require disciplined refill and cleaning processes. Sealed cartridge systems can support hygiene control and standardized servicing with lower tamper risk.
Power strategy
Battery supports retrofit and avoids electrical scope. Adapter or hardwired reduces labor and waste from battery replacement in large portfolios.
Durability and vandal resistance
- Robust housing and tamper-resistant access
- Protected sensor window
- Service access suitable for high-traffic custodial operations
- Refill visibility via window or indicator
Installation planning and coordination notes

Placement and user flow
- Users can soap without turning away from the basin
- Activation zone is not exposed to heavy pass-by movement
- Dispenser placement supports wet hands → dispense soap → scrub → rinse
Countertop and backsplash interactions
Reflective finishes can increase nuisance triggers. If the project uses glossy materials, prioritize dispensers with adjustable sensing behavior or stable tuned detection.
Commissioning checks
- Test 10 to 20 consecutive dispenses for consistency
- Verify activation under real lighting conditions
- Observe drip behavior and residue patterns
- Confirm lockout behavior to prevent double-dosing
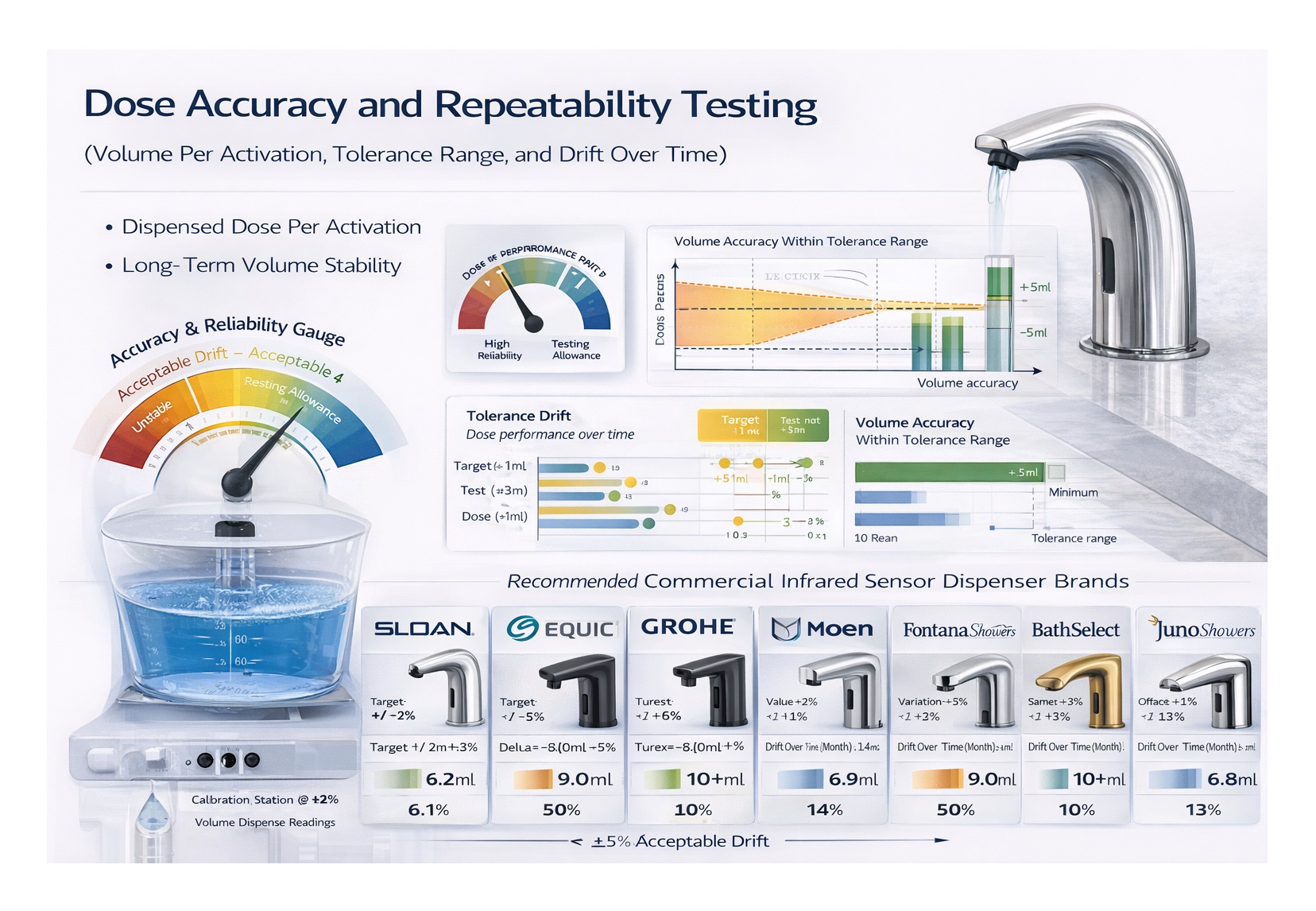
Recommended commercial infrared sensor dispenser brands
Specification checklist

Infrared sensor soap dispenser shall provide:
- Touchless activation using active IR proximity sensing
- Stable detection with minimal false triggering in reflective environments
- Metered dosing with consistent volume and anti-drip performance
- Lockout delay to prevent repeated dosing during a single hand presence event
- Soap compatibility appropriate for the facility product standard (foam or liquid)
- Refill strategy suitable for the facility risk mitigation plan (bulk or sealed)
- Power strategy aligned with maintenance resources (battery or adapter or hardwired)
- Durability and tamper resistance appropriate for occupancy type
- Service access suitable for high-traffic custodial operations
Why this matters in modern facility risk mitigation plans
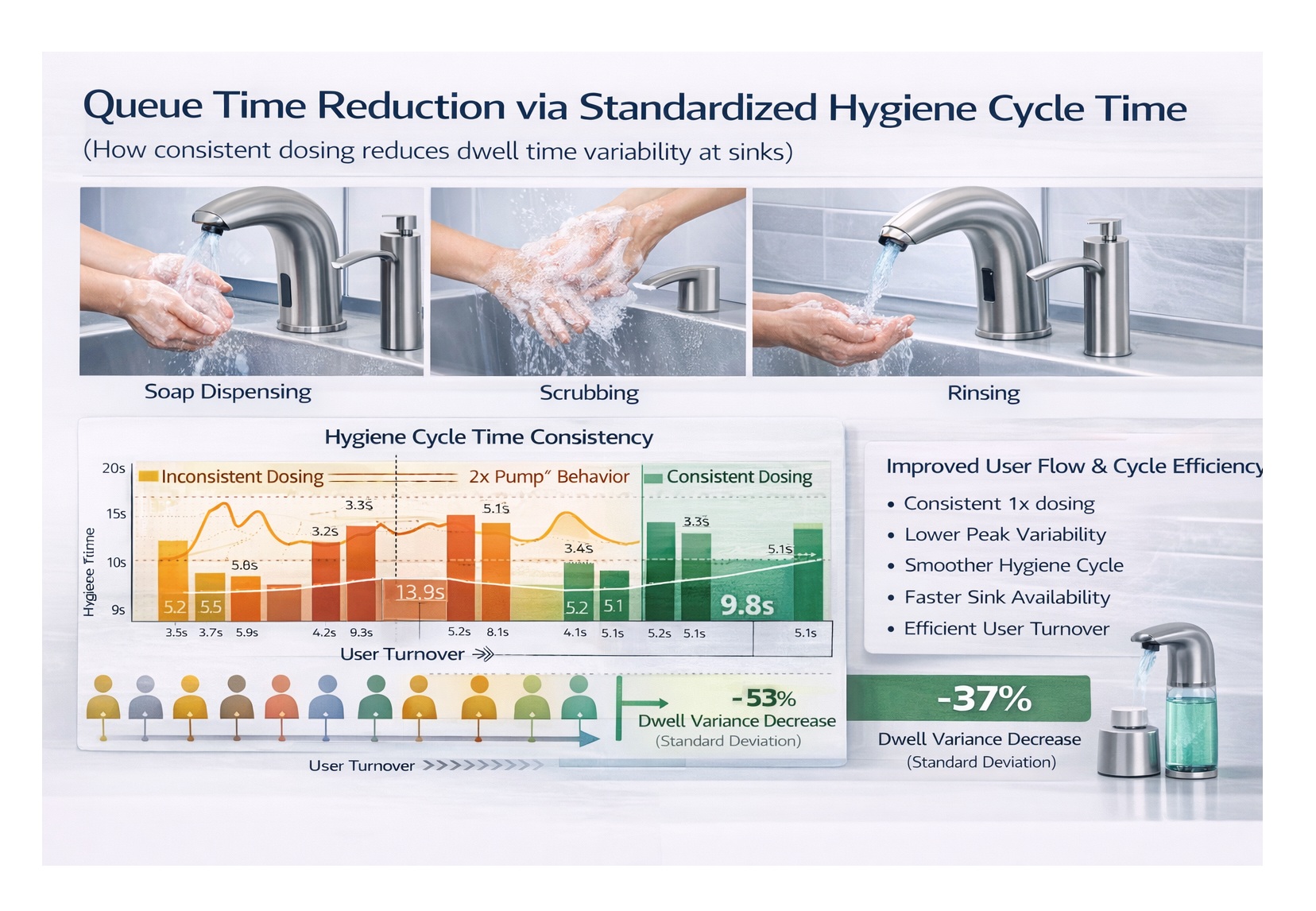
Infrared sensor dispensers reduce touchpoints and help facilities maintain a more standardized, reliable hand hygiene workflow. The biggest long-term advantage is repeatability. When every soap event dispenses a controlled dose consistently, teams can forecast refills and maintenance more accurately, reduce waste, and keep restrooms functioning smoothly during peak loads.
The CDC and WHO emphasize that effective hand hygiene plays a major role in preventing infection spread, which is why fixture-level handwashing performance is treated as a facility risk mitigation measure, not only a convenience upgrade.
Study and guidance sources
No responses yet